Comprehensive Architecture of CXL Type 3 Device
Introduction
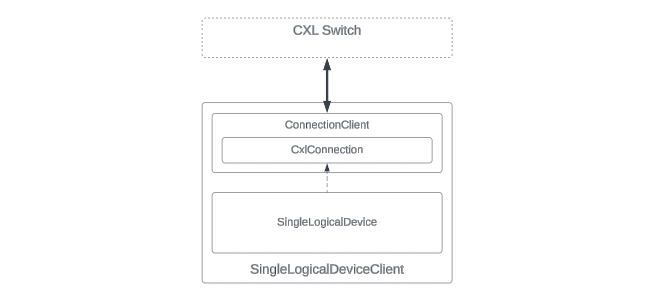
OpenCIS is carefully designed to provide a strong platform for
emulating CXL devices. Within this ecosystem, the Python class
SingleLogicalDeviceClient acts as a high-level model for a CXL type 3 single
logical device.
High-Level Components
This part of the article looks into the structure of the
SingleLogicalDeviceClient class from OpenCIS. It focuses on two main
parts: the ConnectionClient and the SingleLogicalDevice classes. The
ConnectionClient class is important for making TCP socket connections with the
CXL Switch. These connections are key for moving data packets that are vital for
the device's communication. The class not only establishes these connections but
also manages the flow of data, ensuring smooth communication between the CXL
type 3 device and the CXL switch.
The SingleLogicalDevice class includes three layers, each designed for its
effective working. These layers handle different kinds of data packets, adjust
device settings, and imitate the physical parts needed for the operations of a
CXL Type 3 device. This organized setup ensures the device works as per CXL
standards.
ConnectionClient Class
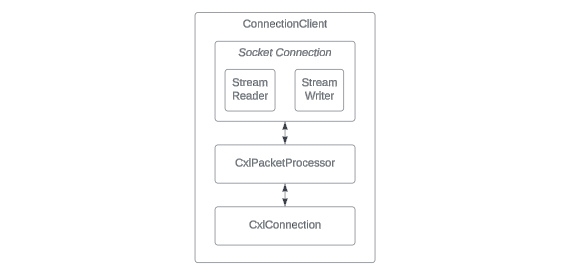
TCP Socket Management
The ConnectionClient class has a key role in setting up and keeping TCP socket
connections with the CXL Switch. This facilitates the important movement of
transaction layer packets in OpenCIS.
Packet Routing
In the ConnectionClient class, the role involves more than just managing. It
includes actively directing packets. This means receiving packets through the
TCP connection and sending them to the right FIFOs in the CxlConnection class
for processing. It also involves taking packets from these FIFOs that need to go
to the host and sending them back through the TCP socket. This two-way routing
ensures smooth communication between the device and the host.
Scalability and Communication
The ConnectionClient class is designed to be scalable, which means it can
easily include new devices into OpenCIS. Its packet routing system
supports a stable and reliable communication network, which is essential for
handling complex operations managed by the SingleLogicalDeviceClient.
SingleLogicalDevice Class
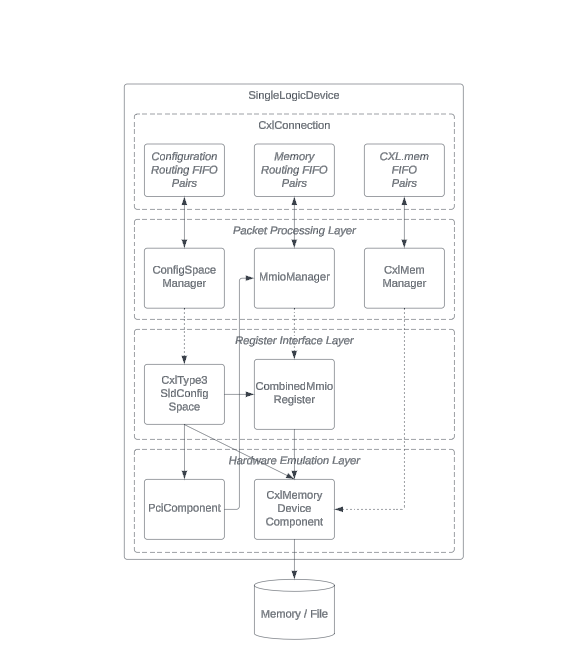
Packet Processing Layer
The core of the SingleLogicalDevice class is the Packet Processing Layer.
This includes the ConfigSpaceManager, MmioManager, and CxlMemManager
classes. Each of these managers deals with specific types of packets, ensuring
complete coverage of CXL Type 3 device operations.
Register Interface Layer
Below the Packet Processing Layer is the Register Interface Layer. This
layer contains the CxlType3SldConfigSpace and CombinedMmioRegister classes.
These classes process packets from the upper layer and access emulated hardware
logic when needed.
Hardware Emulation Layer
The base layer, Hardware Emulation Layer, consists of the PciComponent and
CxlMemoryDeviceComponent classes. These simulate the necessary behaviors for
CXL Type 3 device operations. This layer makes sure that interactions with the
registers result in the right hardware actions according to the CXL
specification.
The SingleLogicalDevice class shows a well-structured approach to handling CXL
packets, register interactions, and hardware imitation. The Packet Routing
feature within the ConnectionClient shows the efficiency of OpenCIS in
managing complex data exchanges.
In-depth Analysis of SingleLogicalDevice Class
The SingleLogicalDeviceClient class includes the SingleLogicalDevice class,
which is made for handling operations specific to CXL Type 3 devices. This
structure is divided into different layers, each playing a crucial role in
ensuring efficient and correct processing of packets as per CXL specifications.
[Figure 2]
Packet Processing Layer
The Packet Processing Layer, a key part of the SingleLogicalDevice class, is
responsible for getting and processing CXL packets, using registers for precise
operations.
ConfigSpaceManager Class
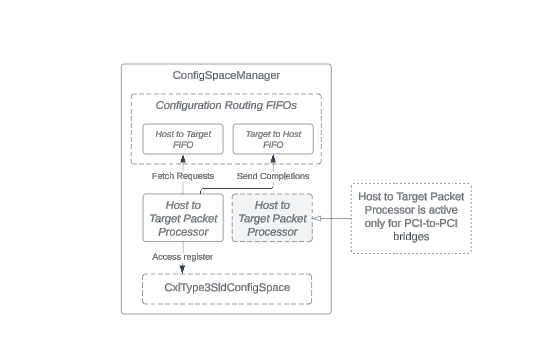
The ConfigSpaceManager class manages Configuration transaction packets. It
uses these packets to set up and control the device according to PCI Express and
CXL specifications.
MmioManager Class
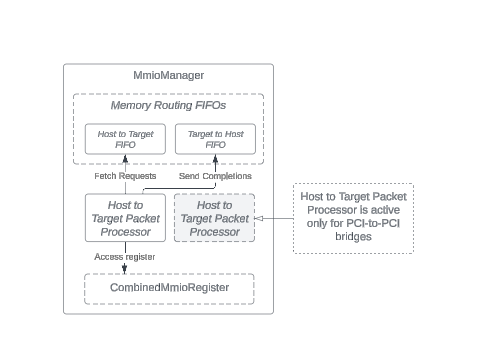
The MmioManager class handles memory-mapped IO requests. It changes memory
requests aimed at the device's base address registers and accesses MMIO
registers set up for a CXL type 3 device.
CxlMemManager Class
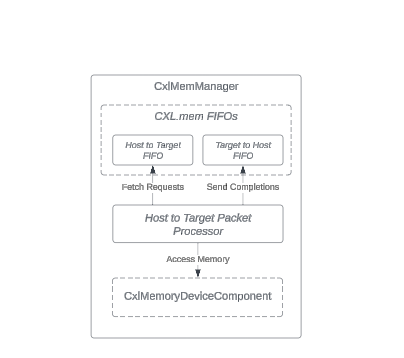
The CxlMemManager class deals with CXL.mem packets, important for reaching
host-managed device memories in CXL type 3 devices. It works with the
CxlMemoryDeviceComponent class, changing CXL.mem operations into actions that
access memories in the CxlMemoryDeviceComponent class.
Register Interface Layer
This layer is the control center, using registers to carry out tasks based on incoming CXL packets.
CxlType3SldConfigSpace Class
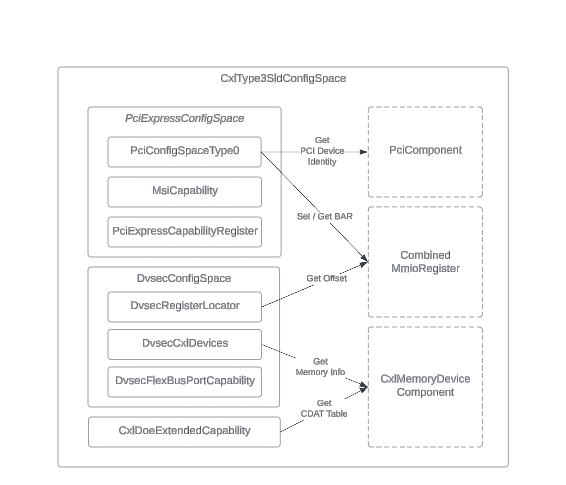
The CxlType3SldConfigSpace class in the SingleLogicalDevice is a set of
configuration registers for a CXL type 3 device. These registers define how the
device is set up and controlled. The DVSEC registers, unique to CXL Type 3
devices, extend their capabilities beyond standard PCIe devices. These
registers allow a CXL host to manage advanced features of CXL Type 3 devices.
The ConfigSpaceManager class uses these registers to modify the device's
behavior based on PCI configuration requests, ensuring it follows the CXL
specification.
CombinedMmioRegister Class
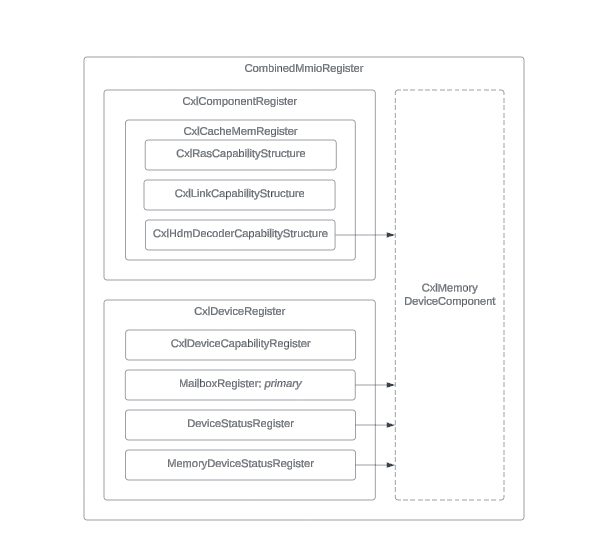
The CombinedMmioRegister class, used in the MmioManager class, is important
for handling CXL operations in CXL Type 3 devices. These are shown to the
device's base address registers (BARs), allowing device configurations through
memory requests to the addresses shown by the BARs.
The CxlType3SldConfigSpace and CombinedMmioRegister classes show the
SingleLogicalDevice class's capability to meet the needs of CXL Type 3
devices, especially in imitating CXL Component Registers and
CXL Device Registers.
Hardware Emulation Layer
The Hardware Emulation Layer accurately simulates the hardware behaviors necessary for a CXL Type 3 device's functionality. This layer turns software-driven configurations and commands into simulated hardware actions.
PciComponent Class
This component simulates standard PCI device interfaces and functions as per PCI Express standards, ensuring the CXL Type 3 device fits well into OpenCIS.
CxlMemoryDeviceComponent Class
The CxlMemoryDeviceComponent class is designed to imitate behaviors needed for
managing host-managed device memory (HDM) operations in a CXL Type 3 device. It
cooperates with the CxlMemManager class to handle memory protocol interactions
for HDM read/write requests.
The cooperation between the Register Interface Layer and the
Hardware Emulation Layer, especially with the CxlMemoryDeviceComponent
class, is vital for carrying out HDM operations, making sure that commands and
configurations related to HDM are properly applied in the emulated environment.
Detailed Features of CxlMemoryDeviceComponent Class
The CxlMemoryDeviceComponent class is essential for the functioning of CXL
Type 3 devices, focusing on configuration through registers and processing
memory requests. It is organized into two main groups:
Configuration and Communication, and Memory Management.
Configuration and Communication
Event Manager
This part processes Component Command Interface (CCI) Event command sets, allowing the device to respond correctly to system events.
Log Manager
It manages CCI Log command sets, important for keeping system logs for diagnostics and monitoring.
CXL Mailbox
This enables communication between the device and the host, allowing for the exchange of commands and information.
CDAT Entries
The Coherent Device Attribute Table (CDAT), accessible through PCI Express Data Object Exchange (DOE), provides important details on memory attributes and latency, key for managing coherent memory access.
Memory Management
HDM Decoder Capabilities and Manager
This function converts Host Physical Address (HPA) to Device Physical Address (DPA), ensuring correct memory addressing and access.
Memory Accessor
It allows access to emulated memory devices via DPA, facilitating read/write operations needed for memory management.
Memory Device Status
This offers real-time status information about the CXL Type 3 device, important for monitoring and managing operations.
Memory Device Identity
It provides identification details for the CXL Type 3 device, helping in its recognition and setup within OpenCIS.
The CxlMemoryDeviceComponent class's organization into
Configuration and Communication, and Memory Management emphasizes its
crucial role in the operations of CXL Type 3 devices. These functions support
efficient working, from processing command sets and enabling communication to
managing memory operations and providing device information.
Conclusion
This article has explained how CXL Type 3 devices function within the
OpenCIS, focusing on their structure and how they handle data and
operations. The SingleLogicalDeviceClient class models the accurate behaviors
of these devices.
The ConnectionClient class manages connections and data flow effectively,
ensuring smooth device communication. The SingleLogicalDevice class, with its
layered structure, processes data, manages settings, and imitates physical
components. This allows CXL Type 3 devices to work correctly and follow CXL
standards.
In summary, the SingleLogicalDeviceClient class is a prime example of how
OpenCIS can accurately model a CXL component. By carefully organizing and
managing every aspect of the device, OpenCIS ensures these devices
perform their roles as defined by the CXL specification, showing OpenCIS's
importance in the evolution of CXL technology.